The most notable attribute of fiber-optic patch cable is that it utilizes light to transmit data, whereas copper cable relies on electricity. Light is not only the fastest means of transmission, but it enables the cable to weigh less than ordinary copper cable. In other words, fiber-optic cable is designed to be installed in areas where copper cable would be unrealistic.
These details alone demonstrate a number of reasons why fiber-optic cable has become a standard within the market. But still there are many more details to consider when choosing a product.
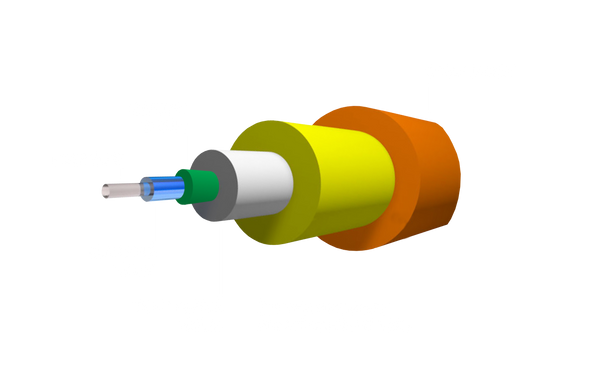
Understanding the Basic Structure
There are several inner layers that make up the fiber-optic cable itself. Understanding the importance of each layer will allow you to consider how each detail may impact your networking demands. There are six essential layers found in fiber-optic patch cables.
The inner core of the fiber-optic cable is made of glass which allows the signal light to travel through. Surrounding the core is cladding which is either made of glass or plastic, and is added as a protective layer that keeps the light inside the core. The 250um coating incases both the fiber core as well as the cladding and is designated to protect each of the inner layers. The 900um buffer layer shields the fiber from outside stress. This layer comes in two types: tight and loose tube. Lastly, the strength members and cable jacket serve as the final two layers and are added to prevent the breakage of all inner layers as the cable is handled and once the cable is installed.
Fiber-optic cable is customizable; the aforementioned factors may alter slightly, depending on the fiber count, capacity, diameter, length, and jacket material required for a particular job.
The Various Types
Distribution fiber cable is a common type of fiber cable because it is designed to be placed within the internal structure of buildings as the “backbone” or for inter-building campus applications. Our distribution fiber cable comes in Single Mode 9/125 and multimode OM1 62.5/125, OM3 50/125, and OM4 50/125, with strand counts ranging from 2 to 72 strands.
There is Armored Fiber Optic Cable to prevent damage from moisture, rodents, and other environmental conditions both inside and outside. Micro distribution high density fiber cable has the option of being comprised of 2 to 144 strands in order to enhance performance and optimize the allotted space. Dry loose tube fiber is designed for rough terrain underground, harsh climates, and natural abrasions, while aerial fiber is idealized for suspended installation and almost any sort of weather exposure. Broadcast deployable fiber cables and military tactical cable are made for temporary installation; these fiber cables are lightweight, durable, and manufactured for reuse, guaranteeing the wide-reaching transmitting and receiving of signals.
Check out our selection of Bulk Fiber to find products to meet the needs of your next project!
Lucrative Management
In order to get the best function from fiber-optic cable, there must be a system that will sustain the cable. For instance, when networking is involved with distribution cable, we suggest the use of a patch panel to keep the cable organized and protected. Specialty cleaning kits are also sold on the Fiber Savvy website in order to ensure the productivity and longevity of the more delicate fiber-optic cables.
As a Final Point
Fiber-optic patch cable has the ability to increase the speed of transmission and bandwidth range compared to other cable types. Creating faster transmission than standard copper cable, being protected from interference, and having the flexibility for use in a wide range of applications, Fiber Optic Cable has the potential of being a worthwhile investment for individuals and business owners looking to build a successful network. Call our team at FiberSavvy for more information!

